2026 EIA Forecast: Gas Prices Projected to Drop to $3 per Gallon
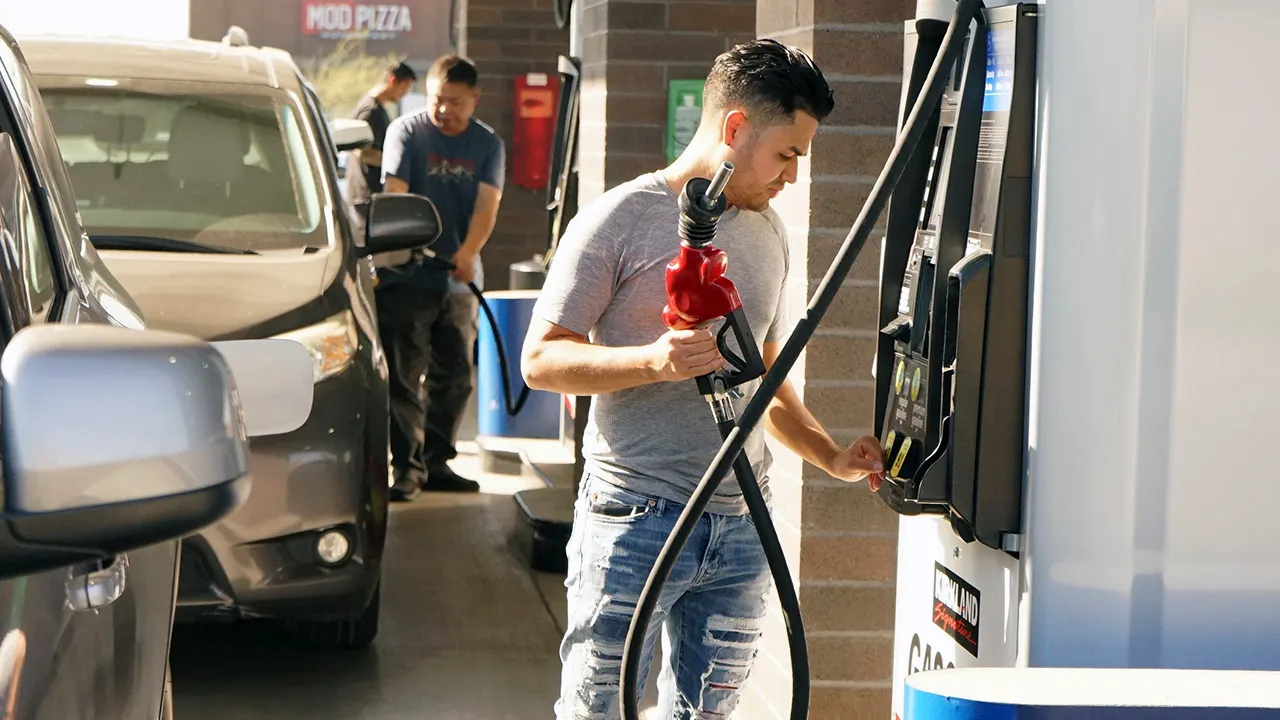
U.S. Energy Secretary Chris Wright discusses falling national average gas prices under President Donald Trump, emphasizing the need for reliable energy in the face of new demands like AI and more on ‘Kudlow.’
Oil and gasoline prices are projected to decline next year, according to a recent forecast from the Energy Information Administration (EIA).
The EIA’s Short-Term Energy Outlook, published in November, indicates that the price of Brent crude oil is expected to drop from $69 a barrel in 2025 to $55 a barrel next year. This forecast is significantly lower than the $81 per barrel average seen in 2024.
Similarly, gas prices are anticipated to continue their downward trend. Retail gas prices averaged $3.30 a gallon in 2024 and are currently at $3.10 a gallon this year. The EIA forecasts a further decline to $3 a gallon by 2026.
U.S. crude oil production has increased this year and is expected to maintain its level through 2026. The EIA reports that the U.S. produced 13.2 million barrels per day in 2024, with projections of 13.6 million barrels per day for both 2025 and 2026.
GAS PRICES DROP BELOW $3 NATIONWIDE AS TRUMP SAYS $2 GAS WITHIN REACH
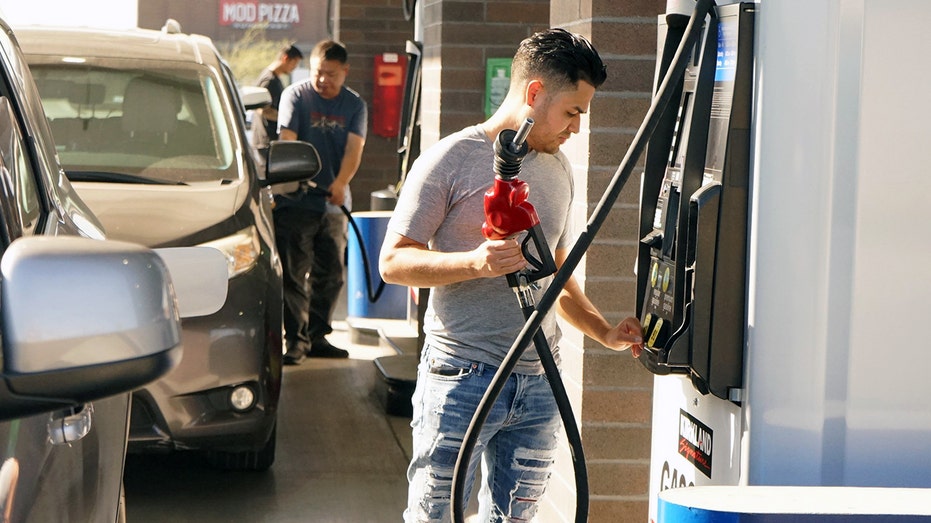
Gas and crude oil prices are projected to decline next year, according to the EIA’s outlook. (Zeng Hui/Xinhua via Getty Images)
Natural gas prices are expected to rise following a significant increase this year. The price at Henry Hub was $2.20 per million British thermal units (BTUs) in 2024 and is projected to rise to $3.50 in 2025, with further increases to $4 in 2026.
In recent years, the U.S. has emerged as the world’s largest exporter of liquefied natural gas (LNG), maintaining its top position in 2023 and 2024. Export levels continue to rise, with the EIA noting that the U.S. exported 12 billion cubic feet per day of LNG last year, increasing to 15 billion cubic feet per day in 2025 and 16 billion cubic feet per day in 2026.
OIL AND GAS DEMAND COULD GROW UNTIL 2050, IEA SAYS

The U.S. led the world in LNG exports in 2023 and 2024, with the export volume projected to rise this year and next. (Stefan Sauer/picture alliance via Getty Images)
The EIA’s report also detailed the share of electricity generation by source across the U.S. Natural gas remains the largest source, accounting for 40% in 2025 and 2026, down slightly from 42% the previous year. Meanwhile, renewables—including hydropower, solar, wind, geothermal, and biomass—accounted for 23% in 2024, with projections of 24% in 2025 and 26% in 2026.

Microsoft is reopening the shuttered Three Mile Island nuclear power plant to help meet rising energy demand due to AI data centers. (Heather Khalifa/Bloomberg via Getty Images)
Nuclear power’s share of the power mix has decreased slightly from 19% to 18% from 2024 to 2025, and it is expected to hold steady at 18% in the upcoming year. Coal’s share of total electricity generation has remained relatively stable, with the EIA reporting it at 16% last year, 17% in 2025, and projecting a return to 16% in 2026.
GET FOX BUSINESS ON THE GO BY CLICKING HERE
The report also highlighted carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, which rose slightly from 4.8 billion metric tons in 2024 to 4.9 billion metric tons this year. The EIA forecasts a return to 4.8 billion metric tons in 2026.
U.S. Energy Secretary Chris Wright discusses falling national average gas prices under President Donald Trump, emphasizing the need for reliable energy in the face of new demands like AI and more on ‘Kudlow.’
Oil and gasoline prices are projected to decline next year, according to a recent forecast from the Energy Information Administration (EIA).
The EIA’s Short-Term Energy Outlook, published in November, indicates that the price of Brent crude oil is expected to drop from $69 a barrel in 2025 to $55 a barrel next year. This forecast is significantly lower than the $81 per barrel average seen in 2024.
Similarly, gas prices are anticipated to continue their downward trend. Retail gas prices averaged $3.30 a gallon in 2024 and are currently at $3.10 a gallon this year. The EIA forecasts a further decline to $3 a gallon by 2026.
U.S. crude oil production has increased this year and is expected to maintain its level through 2026. The EIA reports that the U.S. produced 13.2 million barrels per day in 2024, with projections of 13.6 million barrels per day for both 2025 and 2026.
GAS PRICES DROP BELOW $3 NATIONWIDE AS TRUMP SAYS $2 GAS WITHIN REACH
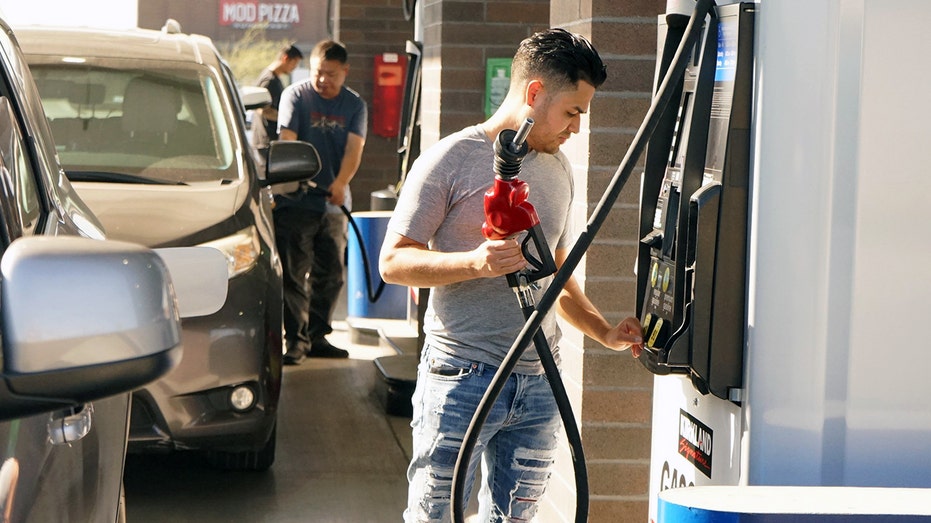
Gas and crude oil prices are projected to decline next year, according to the EIA’s outlook. (Zeng Hui/Xinhua via Getty Images)
Natural gas prices are expected to rise following a significant increase this year. The price at Henry Hub was $2.20 per million British thermal units (BTUs) in 2024 and is projected to rise to $3.50 in 2025, with further increases to $4 in 2026.
In recent years, the U.S. has emerged as the world’s largest exporter of liquefied natural gas (LNG), maintaining its top position in 2023 and 2024. Export levels continue to rise, with the EIA noting that the U.S. exported 12 billion cubic feet per day of LNG last year, increasing to 15 billion cubic feet per day in 2025 and 16 billion cubic feet per day in 2026.
OIL AND GAS DEMAND COULD GROW UNTIL 2050, IEA SAYS

The U.S. led the world in LNG exports in 2023 and 2024, with the export volume projected to rise this year and next. (Stefan Sauer/picture alliance via Getty Images)
The EIA’s report also detailed the share of electricity generation by source across the U.S. Natural gas remains the largest source, accounting for 40% in 2025 and 2026, down slightly from 42% the previous year. Meanwhile, renewables—including hydropower, solar, wind, geothermal, and biomass—accounted for 23% in 2024, with projections of 24% in 2025 and 26% in 2026.

Microsoft is reopening the shuttered Three Mile Island nuclear power plant to help meet rising energy demand due to AI data centers. (Heather Khalifa/Bloomberg via Getty Images)
Nuclear power’s share of the power mix has decreased slightly from 19% to 18% from 2024 to 2025, and it is expected to hold steady at 18% in the upcoming year. Coal’s share of total electricity generation has remained relatively stable, with the EIA reporting it at 16% last year, 17% in 2025, and projecting a return to 16% in 2026.
GET FOX BUSINESS ON THE GO BY CLICKING HERE
The report also highlighted carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, which rose slightly from 4.8 billion metric tons in 2024 to 4.9 billion metric tons this year. The EIA forecasts a return to 4.8 billion metric tons in 2026.




